Research Question 2
Overview
Research Question 2: Does gender influence biochemical responses in hepatitis C patients?
This question explores how biochemical markers, specifically Albumin and Bilirubin, respond differently in male and female hepatitis C patients. These markers are crucial for assessing liver health, and understanding their behavior can aid in more personalized healthcare.
Data Preparation and Analysis
Data Preparation:
We started by refining our dataset to include only relevant variables such as gender, Albumin, and Bilirubin levels, alongside age and hepatitis C status. We rigorously removed records with missing values to ensure the accuracy of our analysis.
Statistical Analysis:
ANOVA and Multiple Regression Models: To assess the influence of gender on liver enzyme levels, we utilized these statistical methods. These models helped us quantify the differences and also explore potential interactions with age, which might modify how gender influences these biochemical markers.
Interaction Effects: We specifically looked for interaction effects between gender and other variables like age to understand if younger or older men and women showed different biochemical responses.
Visualizations:
We created several visual aids, including interaction plots and box plots, to visually represent the data. These visuals help illustrate any apparent differences or trends in how biochemical markers are influenced by gender across different age groups.
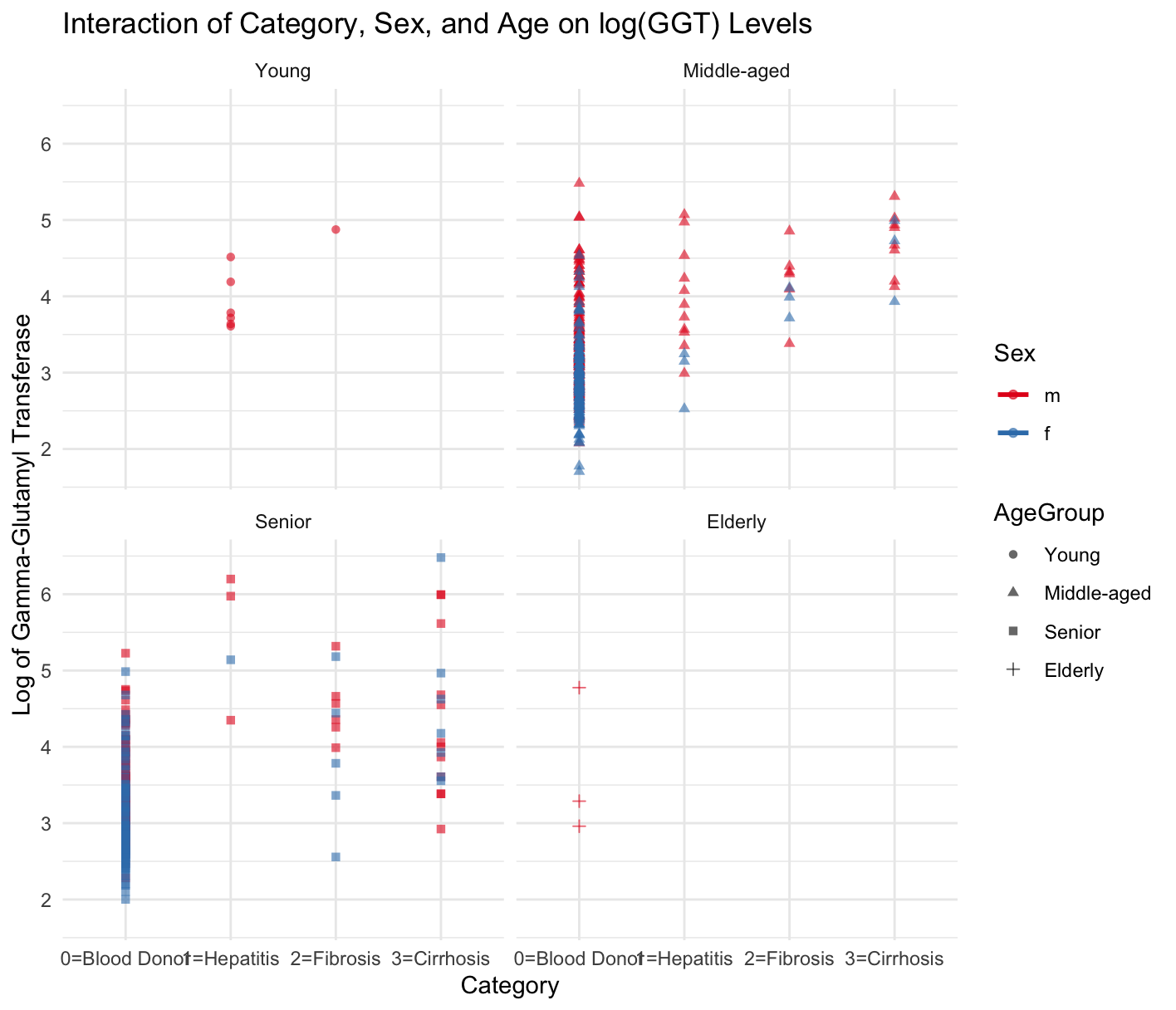
Model Evaluation:
Analysis Outcomes: The primary outputs of our analysis were the ANOVA tables, which provided p-values and F-statistics necessary to determine the significance of the observed differences.
Key Results: The ANOVA results indicated significant gender differences in biochemical responses, with F-statistic values suggesting robust model fit. For instance, the F value for the interaction between gender and age was 6.652 (p < 0.0001), indicating significant interaction effects.
Approaches Considered and Rejected:
Logistic Regression: Initially considered for its simplicity in handling binary outcomes, we ultimately did not use logistic regression because our focus was on continuous biochemical markers.
Complex Multivariate Models: While potentially more robust, these models were deemed too complex for our current analysis scope, potentially complicating the interpretation without providing additional actionable insights.
Real-World Application:
Tailored Treatment Strategies: The insights derived from this analysis are crucial for developing tailored treatment strategies that consider gender differences, potentially improving outcomes for hepatitis C patients.
Enhanced Disease Understanding: This research enhances our understanding of how hepatitis C interacts with biological differences between genders, which can be pivotal in advancing targeted therapy approaches.
Conclusion
Our detailed analysis highlighted important differences in how male and female hepatitis C patients respond biochemically to the infection.
References
UCI Machine Learning Repository: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Dataset. Available at: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/571/hcv+data. This link provides access to the dataset used in your analysis, essential for anyone looking to replicate or extend your research findings.
Professor’s Notes on ANOVA:Unit 3 and Unit 4 Notes: These documents are direct inputs from educational materials provided by your professor, covering detailed theoretical and practical applications of ANOVA, which underpin your analytical methodologies.
Box, G. E. P., Hunter, J. S., & Hunter, W. G. (2005). Statistics for Experimenters: Design, Innovation, and Discovery (2nd Edition). Wiley. A foundational text on the principles of experimental design and analysis crucial for interpreting ANOVA results.
Montgomery, D. C. (2017). Design and Analysis of Experiments (9th Edition). Wiley. Provides a comprehensive resource on experimental design and analysis, supporting the methodologies used in your analysis.
Neter, J., Wasserman, W., & Kutner, M. H. (1996). Applied Linear Statistical Models (4th Edition). McGraw-Hill. Covers regression and analysis of variance in detail, supporting the statistical approaches and tests employed in your research.